信号:操作系统和程序之间初级交流方式
它来自古老的c语言,可以通过man signal查看详情
信号列表:
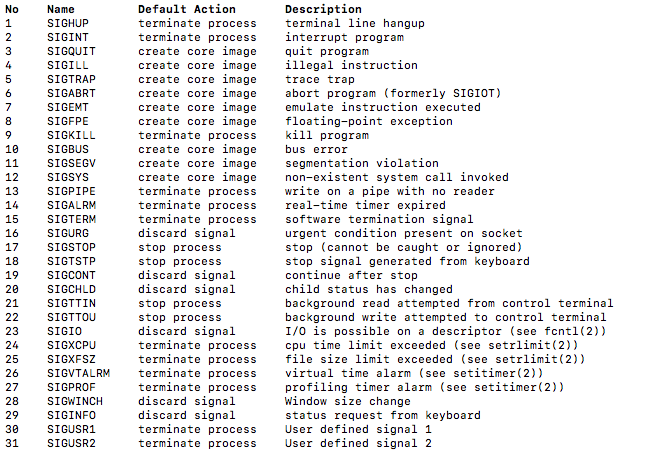
常用的信号有:
SIGINT和SIGTERM都是用来终端程序的SIGUP: 程序后台挂起
Golang也可以处理信号, 示例如下:
package main
import (
"fmt"
"os"
"os/signal"
"syscall"
)
func main() {
// Create the channel where the received
// signal would be sent. The Notify
// will not block when the signal
// is sent and the channel is not ready.
// So it is better to
// create buffered channel.
sChan := make(chan os.Signal, 1)
// Notify will catch the
// given signals and send
// the os.Signal value
// through the sChan
signal.Notify(sChan,
syscall.SIGHUP,
syscall.SIGINT,
syscall.SIGTERM,
syscall.SIGQUIT,
syscall.SIGKILL)
// Create channel to wait till the
// signal is handled.
exitChan := make(chan int)
go func() {
signal := <-sChan
switch signal {
case syscall.SIGHUP:
fmt.Println("The calling terminal has been closed")
exitChan <- 0
case syscall.SIGINT:
fmt.Println("The process has been interrupted by CTRL+C")
exitChan <- 1
case syscall.SIGTERM:
fmt.Println("kill SIGTERM was executed for process")
exitChan <- 1
case syscall.SIGKILL:
fmt.Println("SIGKILL handler")
exitChan <- 1
case syscall.SIGQUIT:
fmt.Println("kill SIGQUIT was executed for process")
exitChan <- 1
}
}()
code := <-exitChan //here blocked
os.Exit(code)
}
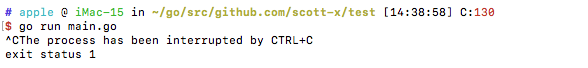
运行代码,可以看到程序是被block住的:

通过按CTRL + C 发送SIGINT信号给程序, 程序退出