熟悉vim的童鞋可能用过很多vim的插件,但是如何实现的呢?
今天以lua的视角来体验一下lua插件的开发过程:
file structure
1.首先,任意位置创建如下目录
.
└── lua
└── luaPlugin
└── init.lua
init.lua中我们随便写点什么:
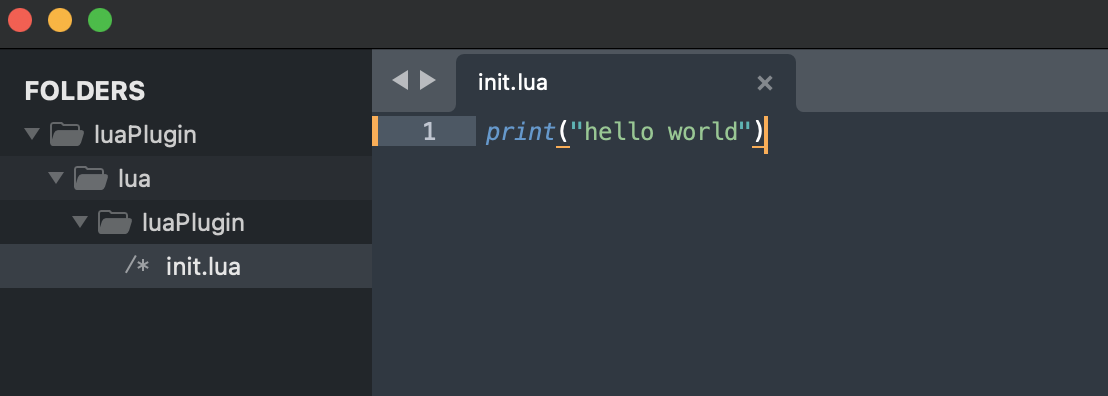
2.如何使这个插件生效呢?
我们需要把插件添加到lua的runtime path中:
# 插件根目录中运行
vim --cmd "set rtp+=./"

接着我们就可以打开vim运行这个插件了
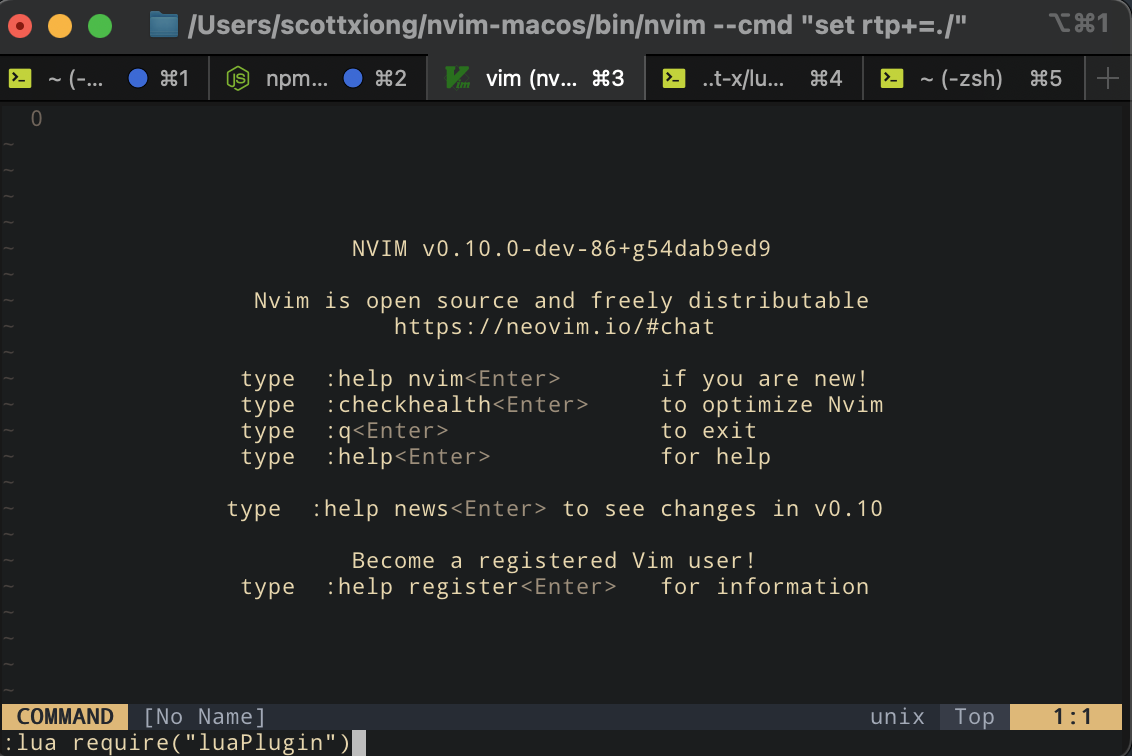
可以看到"hello world"已正常输出
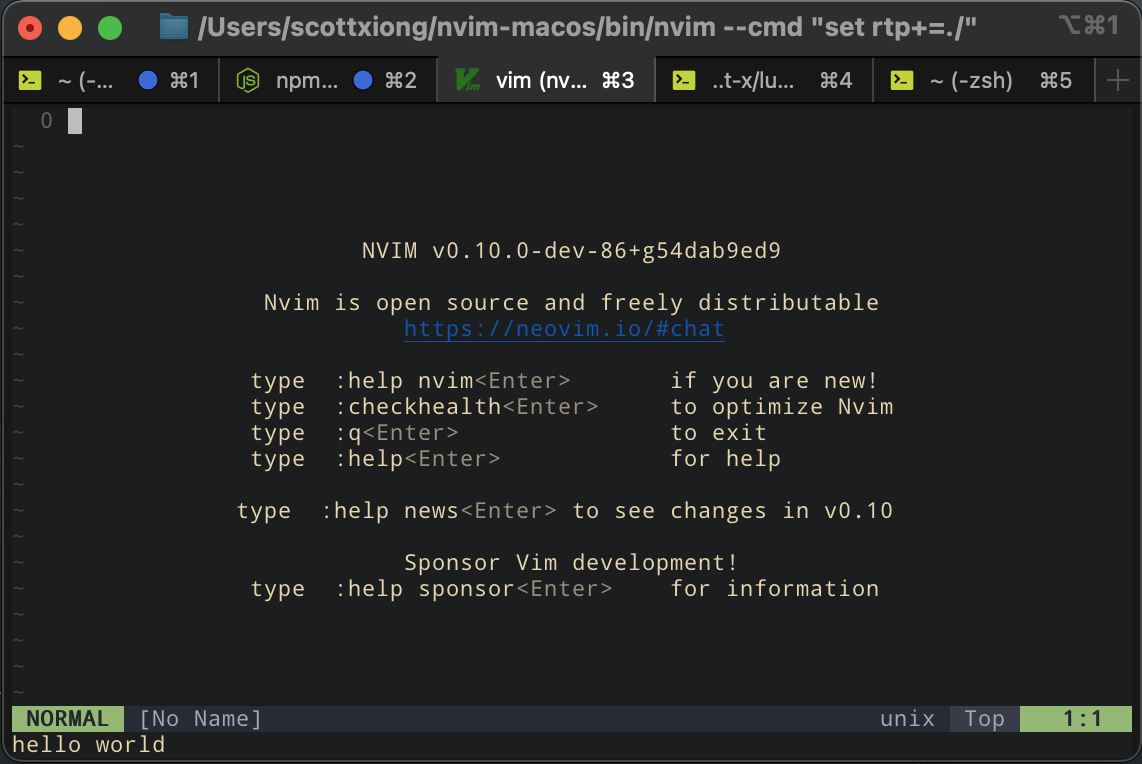
需要注意的是无论你require多少次"hello world"只会输出一次
export function
我们可能会经常看到如下类似的配置:引入一个模块,调用一个function,然后配置leader key

这里暂不讨论lua是如何配置的
init.lua中我们先来定义一个lua function然后导出:
print("hello world")
local function some_function( ... )
-- body
print("hello from function")
end
--important
return {
some_function = some_function
}
接着熟悉的配方,熟悉的套路,先set path下:
# 插件根目录中运行
vim --cmd "set rtp+=./"
接着调用function:
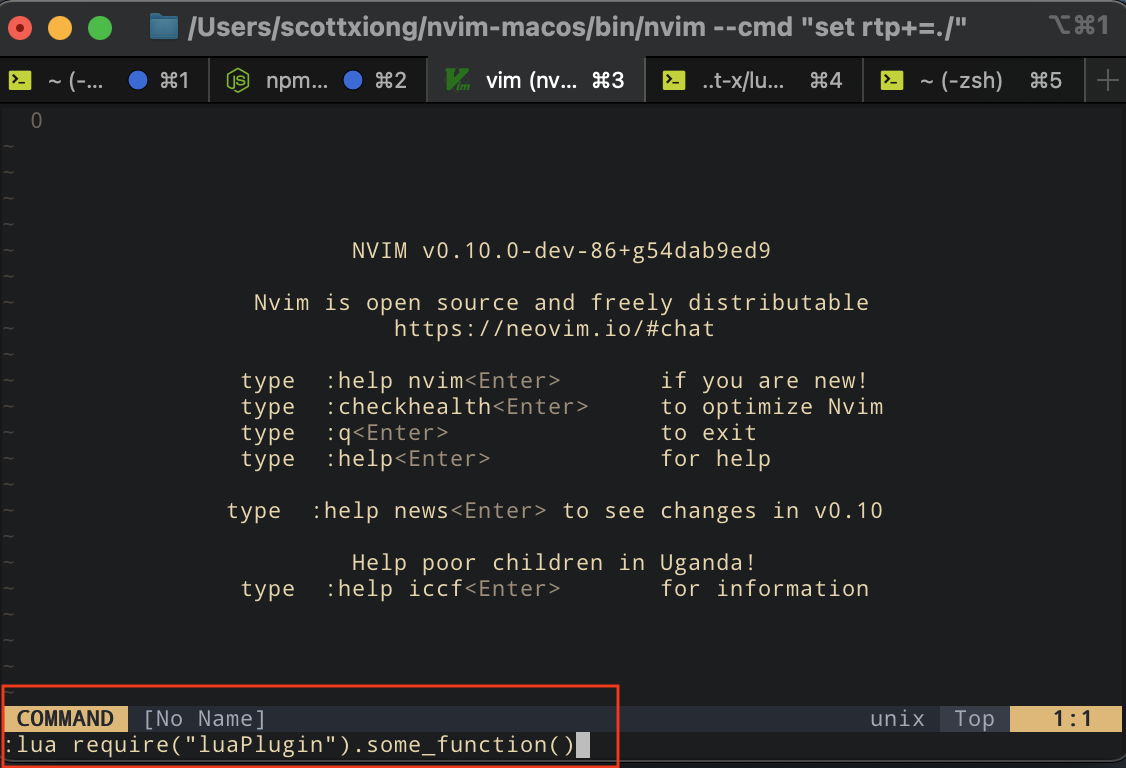
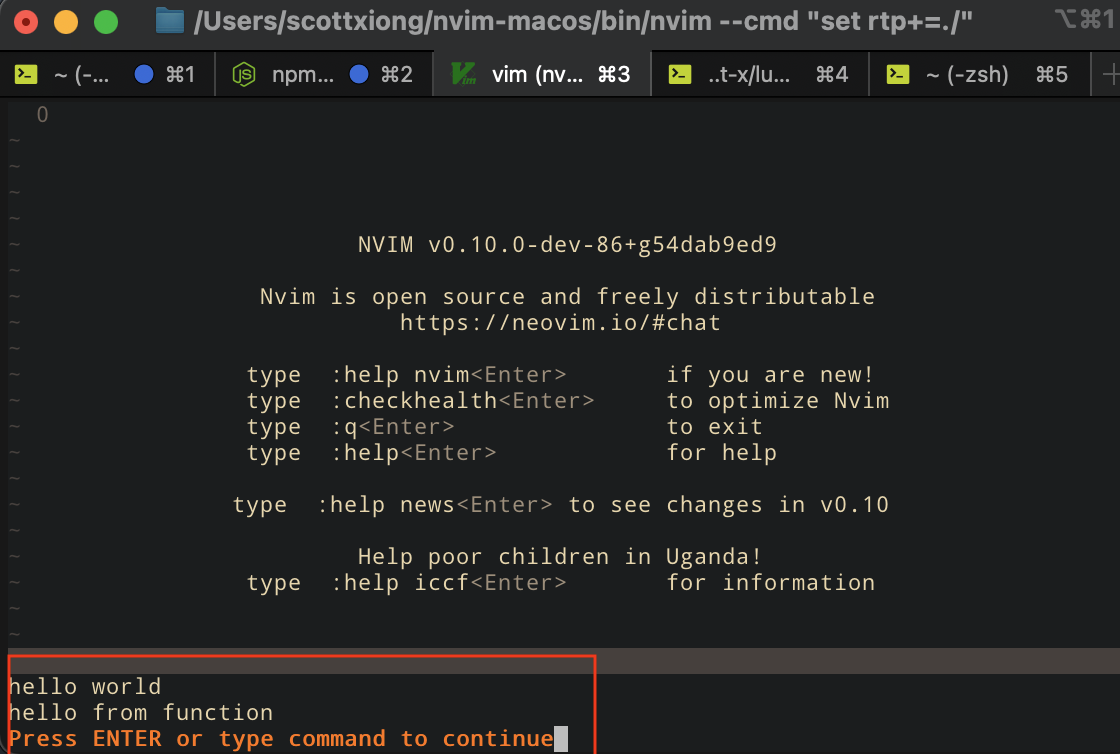
可以看到"hello world"和"hello from function"都输出了:前者是首次加载时才会输出,可以用于初始化;后者是function的调用,每次调用都会执行
interact with vim
更新lua code如下:
local function run_jest( ... )
-- body
local file = vim.fn.expand("%:p")
print("my file is " .. file)
end
--important
return {
run_jest = run_jest
}
然后调用function
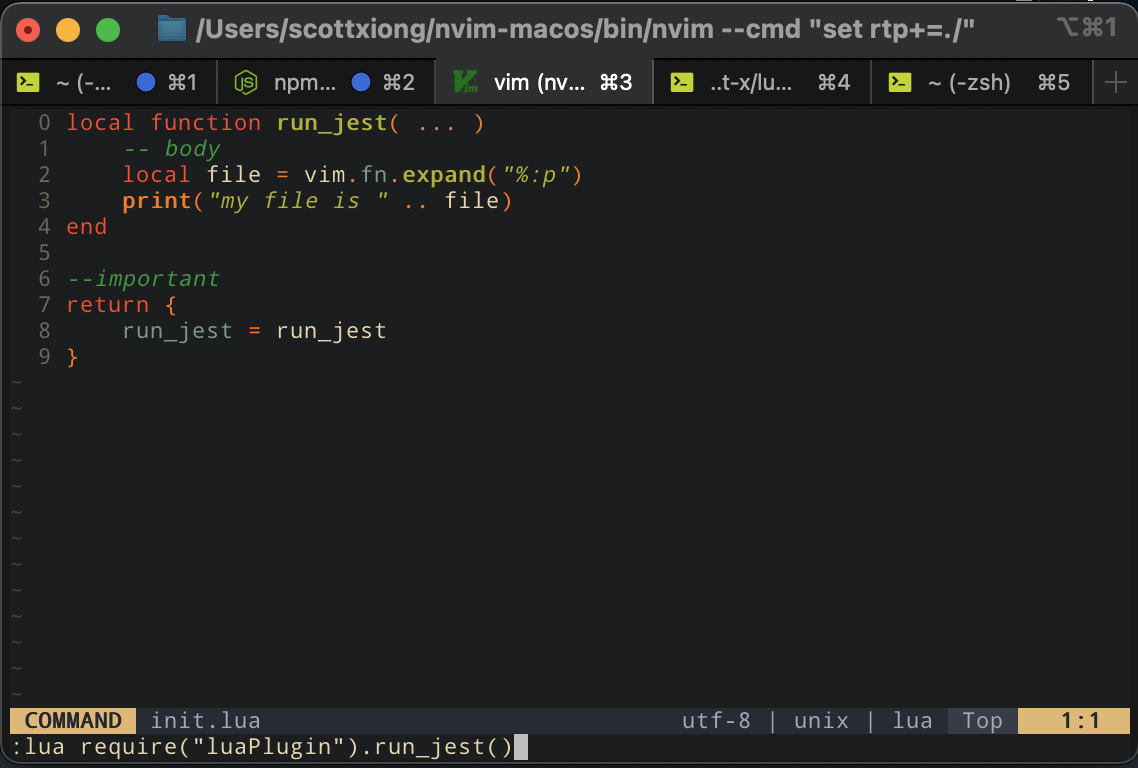
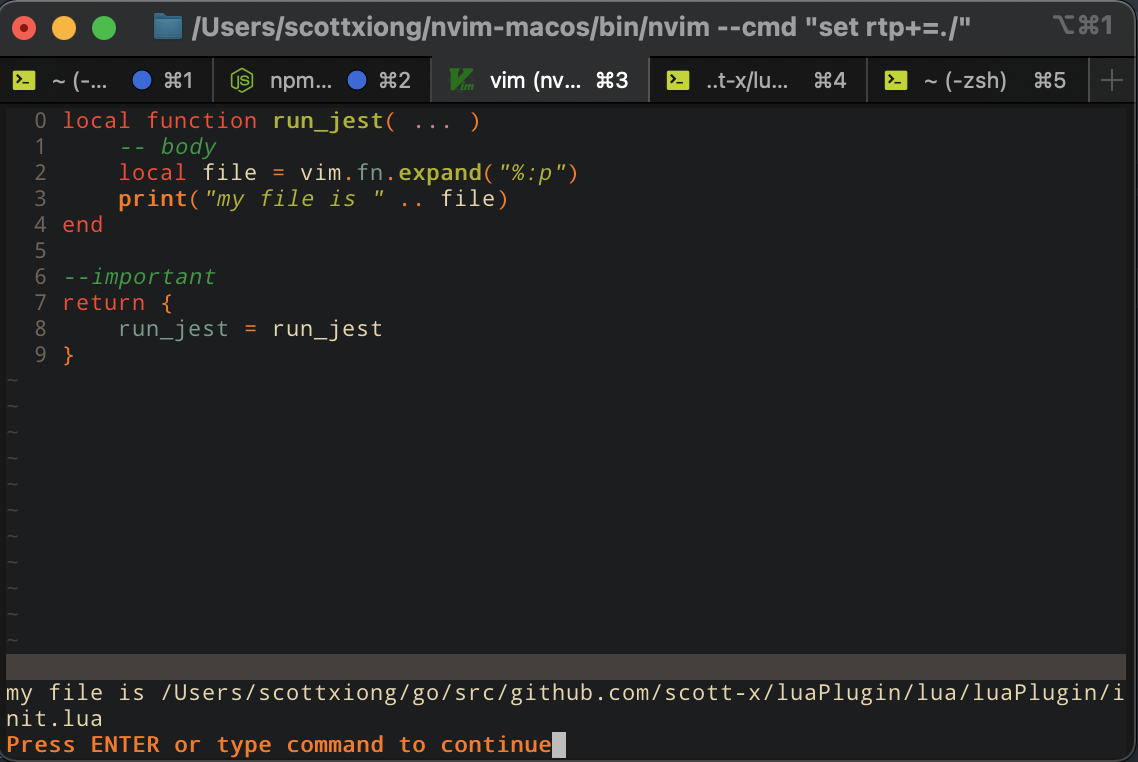
可以看到路径可以正常输出:
新增一句,打开一个新的terminal
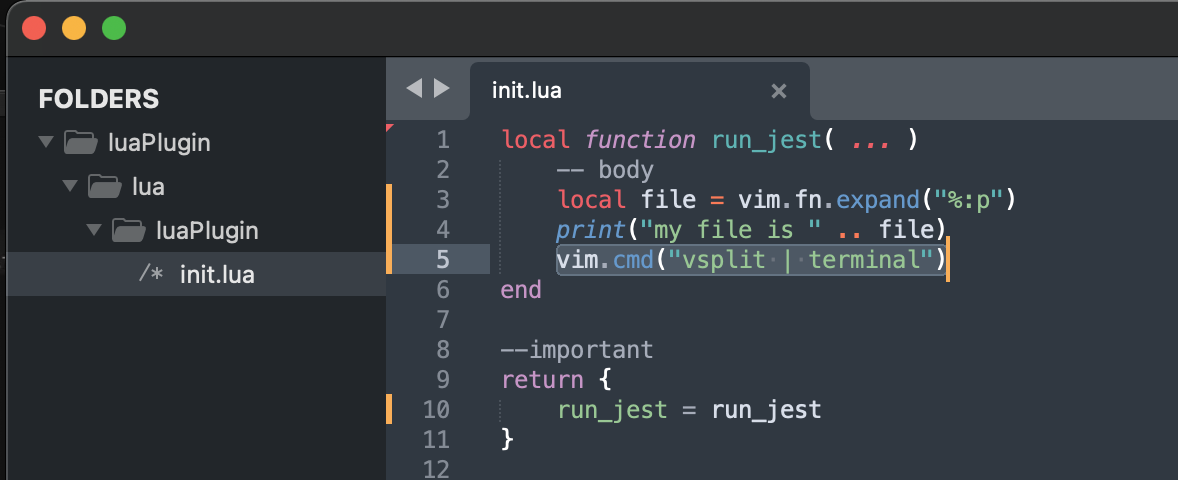
vim运行:
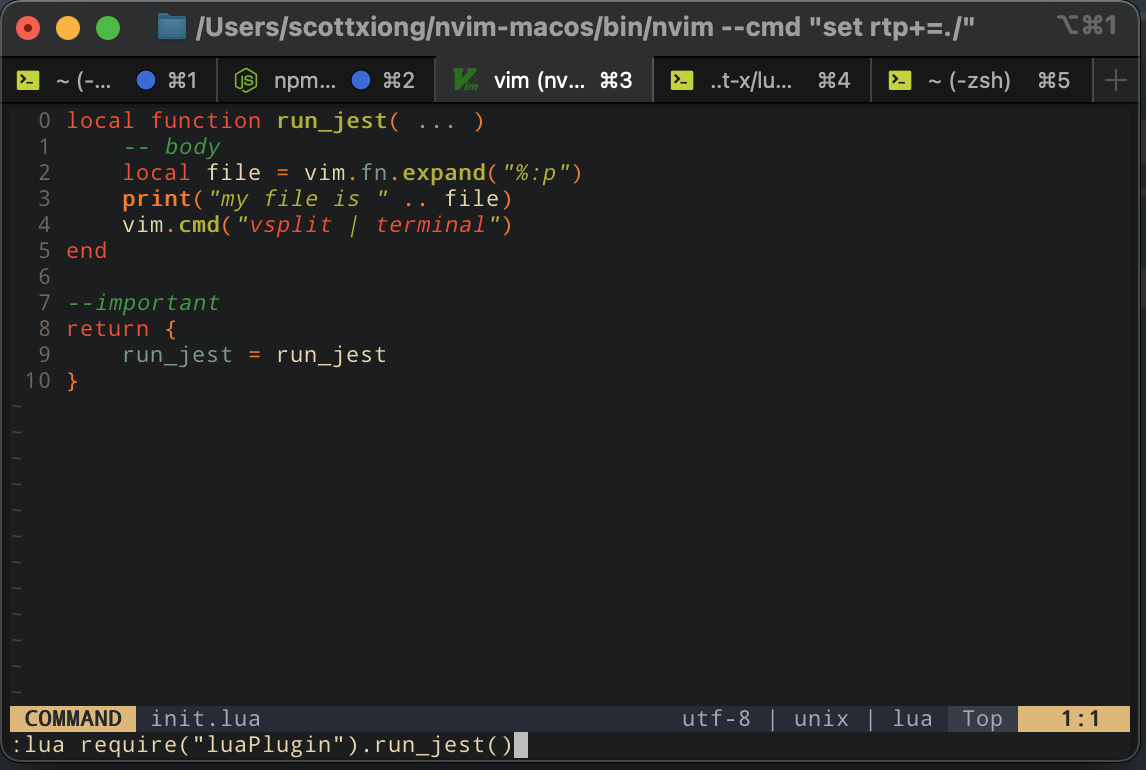
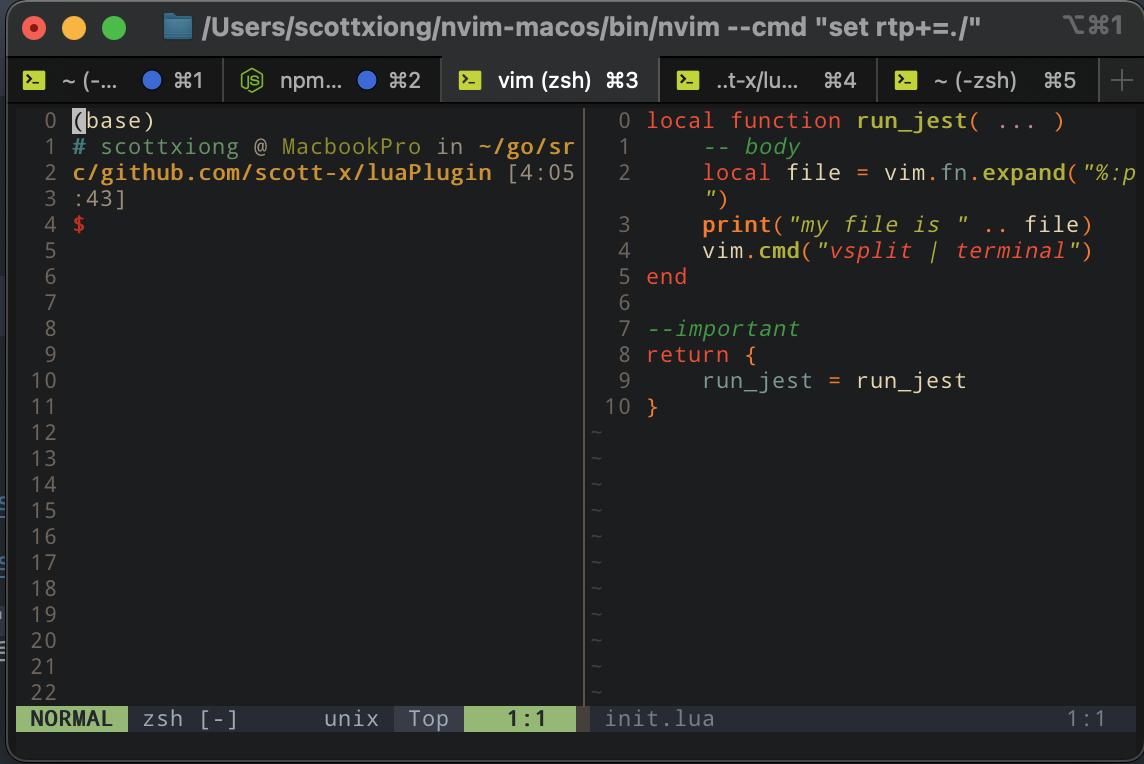
可以看到没有任何问题
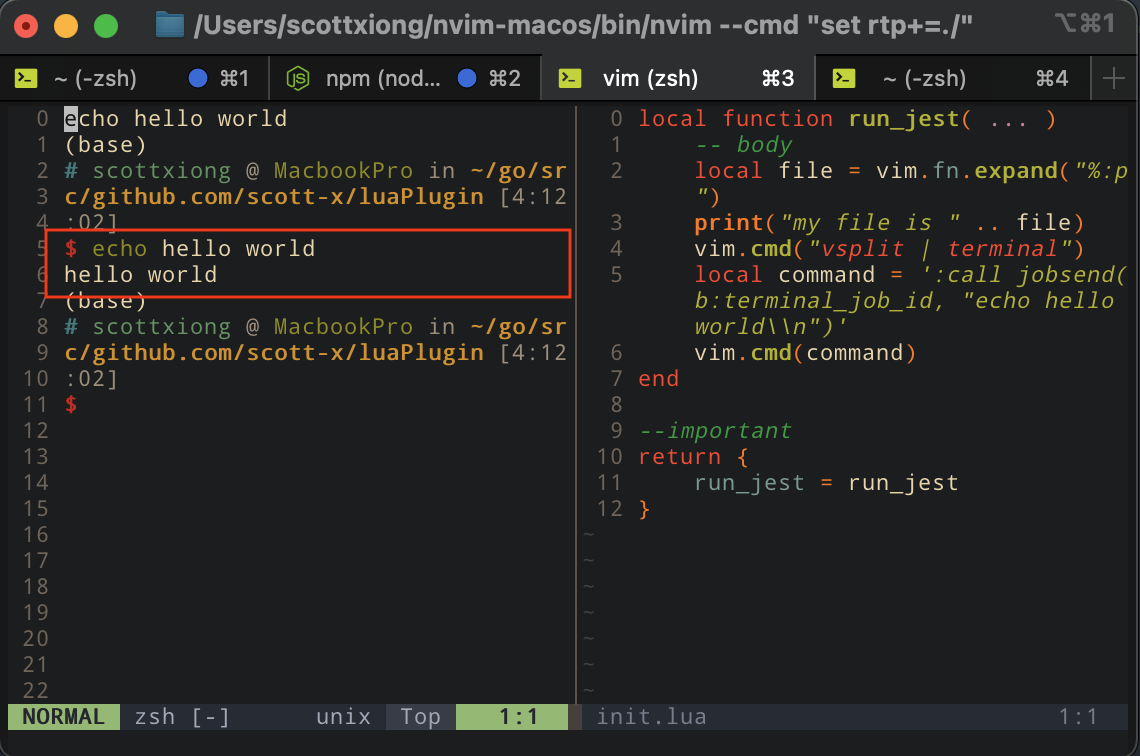
在此基础上, 我们进行深层次的操作,在打开的terminal中输出hello world
local function run_jest( ... )
-- body
local file = vim.fn.expand("%:p")
print("my file is " .. file)
vim.cmd("vsplit | terminal")
local command = ':call jobsend(b:terminal_job_id, "echo hello world\\n")'
vim.cmd(command)
end
--important
return {
run_jest = run_jest
}
运行

新开的terminal正常输出"hello world"(这里有很大的发挥空间,输出测试结果,打印日志信息等)