quick overview
command line
Go is a tool for managing Go source code.
Usage:
go <command> [arguments]
The commands are:
bug start a bug report
build compile packages and dependencies
clean remove object files and cached files
doc show documentation for package or symbol
env print Go environment information
fix update packages to use new APIs
fmt gofmt (reformat) package sources
generate generate Go files by processing source
get add dependencies to current module and install them
install compile and install packages and dependencies
list list packages or modules
mod module maintenance
run compile and run Go program
test test packages
tool run specified go tool
version print Go version
vet report likely mistakes in packages
Use "go help <command>" for more information about a command.
Additional help topics:
buildconstraint build constraints
buildmode build modes
c calling between Go and C
cache build and test caching
environment environment variables
filetype file types
go.mod the go.mod file
gopath GOPATH environment variable
gopath-get legacy GOPATH go get
goproxy module proxy protocol
importpath import path syntax
modules modules, module versions, and more
module-get module-aware go get
module-auth module authentication using go.sum
packages package lists and patterns
private configuration for downloading non-public code
testflag testing flags
testfunc testing functions
vcs controlling version control with GOVCS
Use "go help <topic>" for more information about that topic.
比较常见的command line有:
go run [.]
go run [--race] [xxx.go]
go build [-o target] xxx.go
go mod init [module] #默认以当前文件名为module name
go mod tidy
go test
go get url
go doc
go fmt #我已经对它进行了优化,可以选择用 https://github.com/scott-x/myfmt
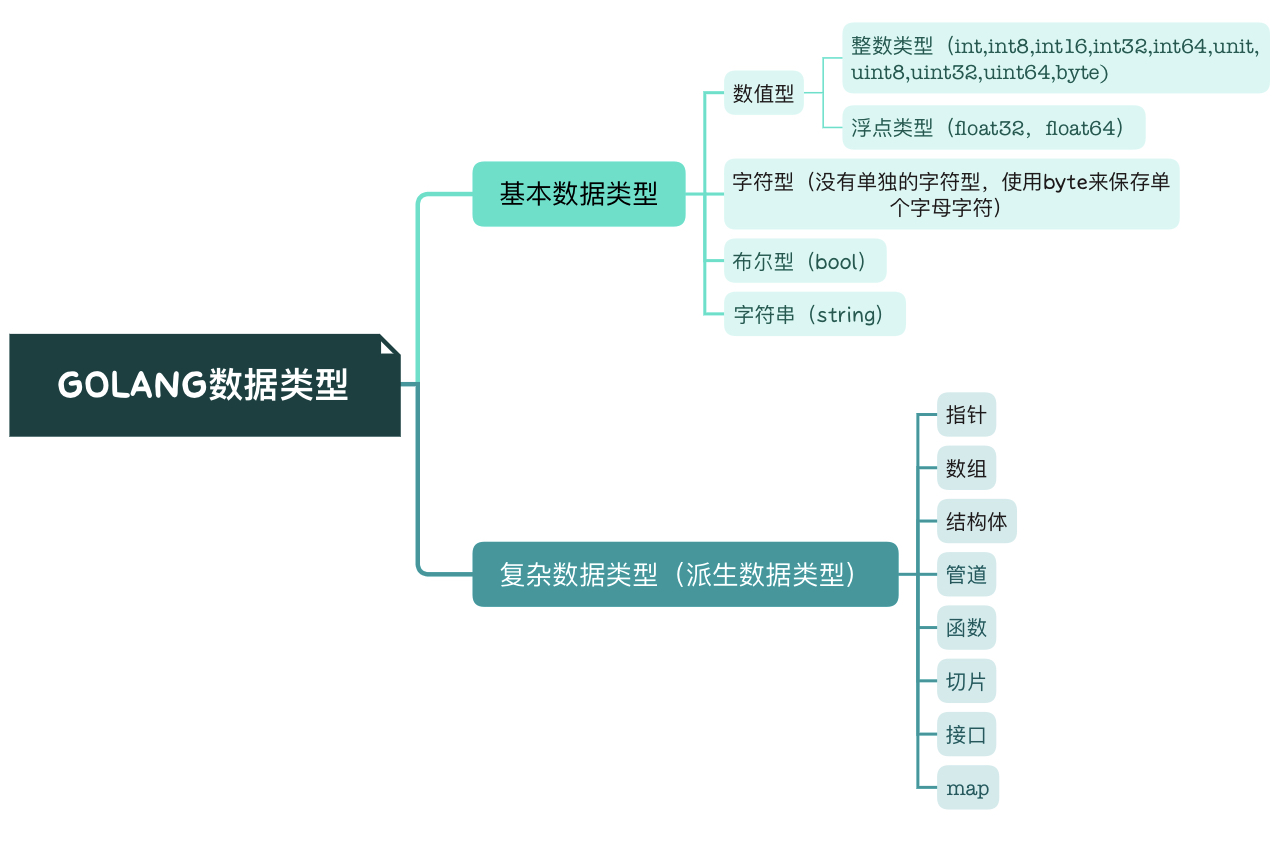
built-in types
- 布尔类型: bool
- 整型: int8,byte,int16,int,uint,uintptr等
- 浮点型: float32,float64
- 复数类型: complex64,complex128
- 字符串: string
- 字符类型:rune
- 错误类型: error
此外,golang也支持以下这些复合类型:
- 指针: pointer
- 数组: array
- 切片: slice
- 字典: map
- 通道: chan
- 结构体: struct
- 接口: interface
上面的数据类型可以归纳到下面这张图中:
zero value
int 0
uint 0
byte 0
float64 0
bool false
string "" (the empty string)
rune 0
struct nil
control flows
Conditionals:
if condition1 {
} else if condition2 {
} else {
}
switch i {
case 0:
case 1:
fallthrough
case 3:
f()
default:
...
}
loops:
//for loop
for i:=0; i<n; i++ {
something
}
---
//for range
for i,v := range array1 {
}
for key,value := range map1 {
}
data structure
当用new去创建slice/array/map/instance的时候,它返回的是第一个元素的指针;当使用make的时候,它返回的是第一个元素
//const vs var
const a = 1
var price, tax float64
var x bool
var y,z int = 1,2
x,y,z := true, 123, "steve"
//array is a fixed number of continuous memory space
//slice is a resizable array
slice1 := []int{}
slice2 := append(slice1, 1)
//make or new slice or array
slice1 := new([]int)
slice2 := make([]int, 10, 20)
slice3 := make([]int, 0)
slice4 := make([]int,10)
//map is key value pair
myMap :=make(map[string]string, 10). //define the length of the map
myMap :=make(map[string]string) //do not have to define the size
myMap["a"]="b" //assign value to its key
//notice that the element of the map could be a function, as follows
myFuncMap :=maps[string]func() int{
"funcA": func() int{return 1},
}
//struct
type Person struct{
Name string
Age uint
address Address
}
type Address struct {
Province string
City string
}
p1 :=new(Person)
p2 :=Person{}
p3 :=&Person{}
type A func(string) error
type B int
visiable & invisiable
首字母大写是可见的,反之不可见;
tips
同一包中: 属性、方法、结构体访问无限制, 可以直接拿来用; 不同包中: 首字母需大写, 其他包方可访问,尤其是结构体